Artificial gravity or rotational gravity is thus the appearance of a centrifugal force in a rotating frame of reference the transmission of centripetal acceleration via normal force in the non rotating frame of reference as.
Floor of orbit frog.
Connects at the front of the mouth human.
Each bone has 3 parts.
Each maxilla also enters into the formation of two fossae.
The bony orbit of all amphibians opens into the roof of the mouth.
Living amphibians share other unique traits.
Szekely in encyclopedia of neuroscience 2009.
In the frog there is a muscle sheet the orbital muscle which separates the orbit from the snout cavity it is innervated by a group of neurons in the upper pole of the 5th nucleus and the axons reach the muscle by way of the ophthalmic and maxillary nerves.
Artificial gravity sometimes referred to as pseudogravity is the creation of an inertial force that mimics the effects of a gravitational force usually by rotation.
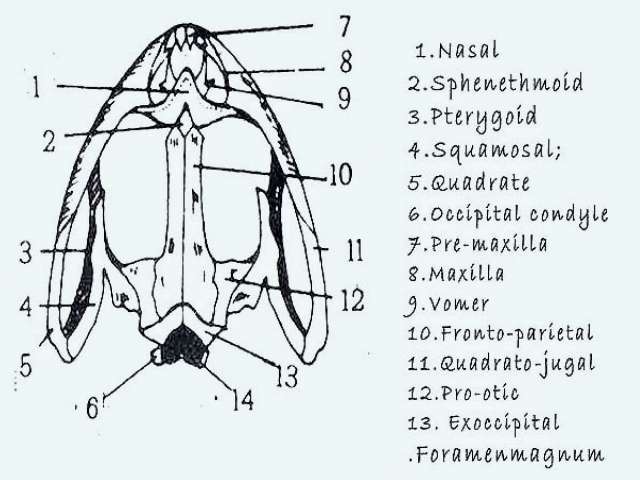
Supratemporal arch is present.
16 1 or frog is a typical vertebrate.
Start studying skeletal system of a frog.
Inside the mouth floor for the eyeballs.
9 in the middle of the cranium laterally two orbits are present.
Palatine runs through the floor of the orbit and innervates the roof of the mouth cavity.
The jugal bone forms the ventral border of the orbit.
What if the shuttle pilot played by tom hanks glances out the window and notices that a small meteor has punched a hole in one of the tanks causing suspended frog sperm to spew into space forming a frozen chunk that could some day fall out of orbit with the friction of atmospheric re entry turning it into a steaming glowing glob.
On either side of the cranium is large gap orbit which lodges the eye.
Connects to the front of the mouth.
A long arm that forms the lateral wall of the orbit.
When the tender bones of the upper jaw and lower nostril are severely or repetitively damaged at any age the.
Muscle inside the mouth on the lower jaw.
Flips out in order to catch food.
Satellite neurons to the facial trigeminal nuclear complex.
The infratemporal and pterygopalatine and two fissures the inferior orbital and pterygomaxillary.
The floor and lateral wall of the nasal cavity.
In structural organisation the toad fig.
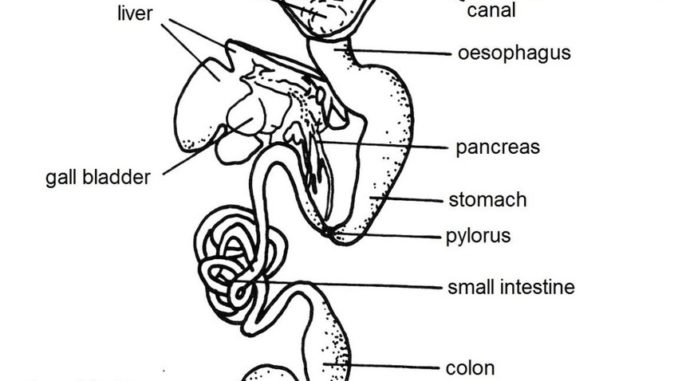
A place where the frog can exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide.
A short arm that contacts the rear end of the frontoparietal and a long posterior arm that connects to the hind end of the qudratojugal bone.
All have fat bodies that develop from the germinal ridge of the embryo and retain an association with the gonads in adults.
Each orbit is bounded by prefrontal supra orbital lacri mal post frontal and jugal bones.
Both are most common throughout india.
Inside the mouth floor for the eyeballs.
Floor of the orbit.
Stores bile produced by the liver.
Only used when frog is highly active.
The wall of the orbit.
To gain a first hand knowledge in vertebrate anatomy students are asked to dissect toad or frog at the very beginning.
Different between human and frog tongue.
Connects to the front of the mouth.
Inside the mouth on the lower jaw.
Connects at the back of the mouth.