The mylohyoid genioglossus and geniohyoid muscles comprise the muscular floor of the oral cavity.
Floor of oral cavity is innervated by.
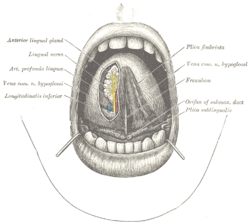
The floor of the oral cavity receives sensory innervation from the lingual nerve a branch of the mandibular v3 division of the trigeminal nerve.
There are several muscles inside the oral cavity.
It is bounded by a roof a floor and lateral walls.
Quizlet flashcards activities and games help you improve your grades.
The vestibule and the oral cavity proper.
All muscles of the tongue are innervated by the hypoglossal nerve xii except the palatoglossus muscle.
The oral cavity is situated anteriorly on the face under the nasal cavities.
The cheeks are innervated by the buccal nerve.
Innervation of the oral cavity study guide by bsbdesja includes 12 questions covering vocabulary terms and more.
The mouth consists of 2 regions.
These behaviors are governed by chemosensory and somatosensory neurons which converge in the mouth.
The posterior part of the oral cavity is referred to as the mouth proper.
The tongue is also innervated by special sensory fibres for taste from the chorda tympani a branch of the facial nerve cn vii.
The vestibule is the area between the teeth lips and cheeks.
The superior border of the oral cavity includes the soft palate that is made up of five different muscles.
Muscles of the soft palate are innervated by the vagus nerve x except for the tensor veli palatini.
The oral cavity is bounded at the sides and in front by the alveolar process containing the teeth and at the back by the isthmus of the fauces its roof is formed by hard palate at the front and a soft palate at the back.
The floor of the oral cavity is made up of the mylohyoid and geniohyoid which act in the elevation of the hyoid laryngeal complex during swallowing.
Tensor veli palatini musculus uvulae levator veli palatini palatopharyngeus.
It is bordered by the hard palate in the upper front while the soft palate constitutes the upper back boundary 10 inferiorly it has various oral muscles glands tongue attachment to the oral cavity floor 7 through the flexible band of tissues known as lingual frenulum 21.
The oral cavity is responsible for a variety of complex behaviors including feeding and speech.
Anteriorly it opens to the face through the oral fissure while posteriorly the oral cavity communicates with the oropharynx through a narrow passage called the oropharyngeal isthmus also termed the.